19 Oct Lymphatic Filariasis
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Lymphatic Filariasis”. This topic has relevance in the Social Issues section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About Lymphatic Filariasis (LF)?
For Mains:
GS 2: Social Issues
Lymphatic Filariasis in India?
Why in the news?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has confirmed that the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR) has successfully eradicated Lymphatic Filariasis (LF).
Context
- Lao PDR has eliminated Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) in 2023, becoming the second country to achieve this milestone after Bangladesh.
- This achievement follows the successful elimination of trachoma as a public health hazard in 2017.
- WHO declared this achievement, marking significant progress in combating neglected tropical diseases (NTDs).
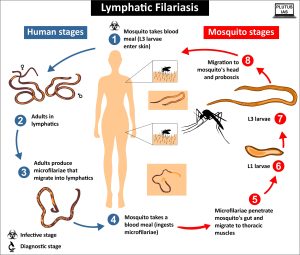
About Lymphatic Filariasis (LF):
- LF, also known as elephantiasis, is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by filarial parasites, including Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and B. timori.
- Culex mosquitoes serve as vectors for transmitting these parasites to humans through mosquito bites.
- The parasites invade lymph vessels, leading to conditions such as hydrocele (scrotal swelling) and lymphedema (swelling due to lymph fluid buildup).
Effective Treatment and Global Progress:
- Mass drug administration (MDA) is the most cost-effective approach to treating LF and preventing its transmission.
- WHO recommends a triple therapy combination of ivermectin (I), diethylcarbamazine (D), and albendazole (A) for MDA against LF.
- Multiple rounds of MDA, covering over 65 percent of the population in LF-endemic areas, are necessary for success.
- Over the last 15 years, the global population requiring LF interventions has decreased by 53 percent due to the Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis initiated in 2000.
Lymphatic Filariasis in India:
- India is actively working to eliminate LF, with certain states bearing a significant disease burden.
- States like Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Bihar account for approximately 60 percent of lymphedema cases in India.
- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched a nationwide campaign called “Sarva Dawa Sevan” or Mass Drug Administration (MDA) in high-burden districts across states like Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Maharashtra.
- India’s goal is to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2027, three years ahead of the global target, showing a strong commitment to combating the disease.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 19th Oct 2023
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Lymphatic Filariasis (LF):
- Lymphatic Filariasis is a mosquito-borne infectious disease
- It is caused by filarial virus
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) and its treatment:
- Culex mosquitoes serve as vectors for transmitting Lymphatic Filariasis to humans through mosquito bites.
- The triple therapy combination for Lymphatic Filariasis includes ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine, and albendazole.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Examine the efforts and challenges faced by India in its quest to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) by 2027.



No Comments