Modem, router and switch, these three things look pretty much the same from the appearance, even if at times they are integrated into a single device, if you think they are the same thing then you are wrong, this article will tell you what they are and how they perform, so you can choose the best one for your needs.
Modem vs. Router vs. Switch: The Basics of Them
What is modem?
A modem is a very important equipment in a computer network, it is a computer hardware that translates computer-generated information into analog signals that can be transmitted by an ordinary telephone line. These analog signals, in turn, can be received by another modem at the other end of the line and translated into a language that the computer understands.
What is router?
A router is a computer network device that transmits packets of data to their destinations through a series of networks,which is a process called routing. A router is a device that connects two or more individual networks, and routing works at the third layer of the OSI model - the network layer, such as the Internet Protocol layer.
What is switch?
Switch is a network device used for electrical (optical) signal retransmission. It provides an exclusive electrical signal path for any two network nodes connected to the switch. The most common type of switch is the Ethernet switch. Other common switches are telephone voice switches, fiber optic switches, and so on.
Modem vs. Switch vs. Router: What's the Difference?
Modems, routers, and switches are unique devices crucial for communication systems. A modem, at the data link layer, converts digital data into analog signals for transmission. Routers work across the data link, network, and physical layers, connecting multiple networks and enabling their communication. Switches operate at the data link layer, facilitating information exchange within the system. Comprehending these differences aids in a deeper, valuable comparison of these devices.
Let‘s check out a table to gain more insights. Below is the comparison table for modem, router and switch.
Hopefully you've gotten an preliminary idea of what these products are, and we'll be doing a pairing comparison to give you a clearer and in-depth understanding.
Modem vs. Router
A modem is a device that modulates an analog signal to convert digital information, while a router is a computer networking device that manages data entering and leaving the network and moving within the network. A modem operates on the data link layer, while a router can operate on the data link, network, and physical layers.
Switch vs. Router
Different working levels: switches mainly work in the data link layer (Layer 2) routers work in the network layer (Layer 3). The basis of retransmission is different: switch retransmission is based on the MAC address. (Physical address) Router is based on IP address. (Network address)
The main function is different: switches are mainly used to set up LANs, while the main function of routing is to connect the LANs set up by the switches to each other, or to access to the Internet. Switches can't split broadcast domains. Router can also provide firewall functionality. Router is more complex to configure than a switch.
Modem vs. Switch
Modems and switches are usually connected together through a router, which can be connected to the modem on one end (ISP) and to the switch on the other end (local network). In terms of their differences, modems are used in home, Internet-connected, and ISP-to-ISP home networking environments, while network switches are most commonly used in large networks, such as businesses, campuses, or data centers.
Modem vs Router vs Switch: What’s the Connection Sequence
There are three types of connections here, but as far as the three devices mentioned are concerned, they should be in order: modem, router and switch.
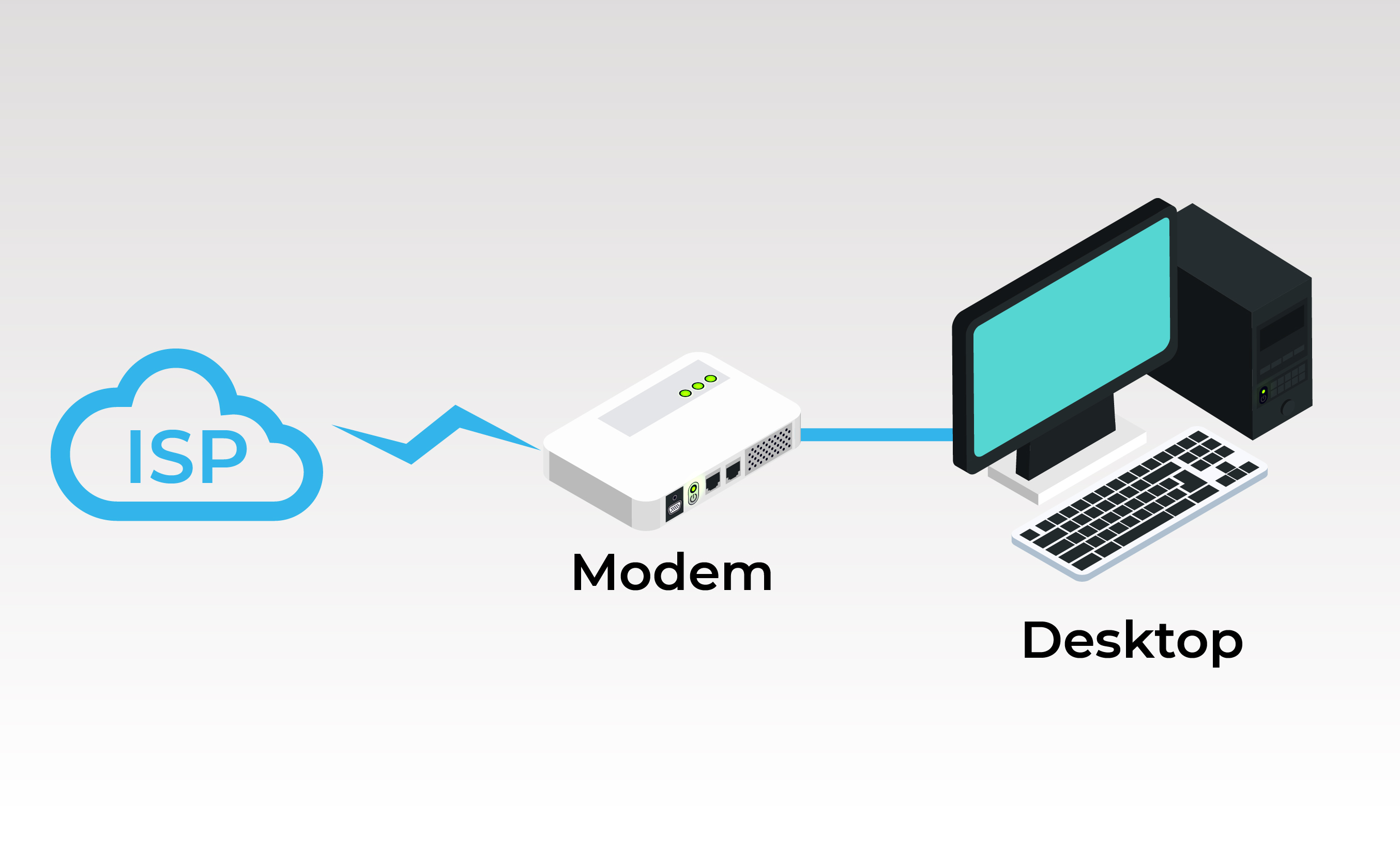
1. ISP——Modem——Desktop
It converts digital signals from computers into analog signals, which are conducted over ordinary telephone lines, and then the analog signals are connected to the Internet through an ISP.
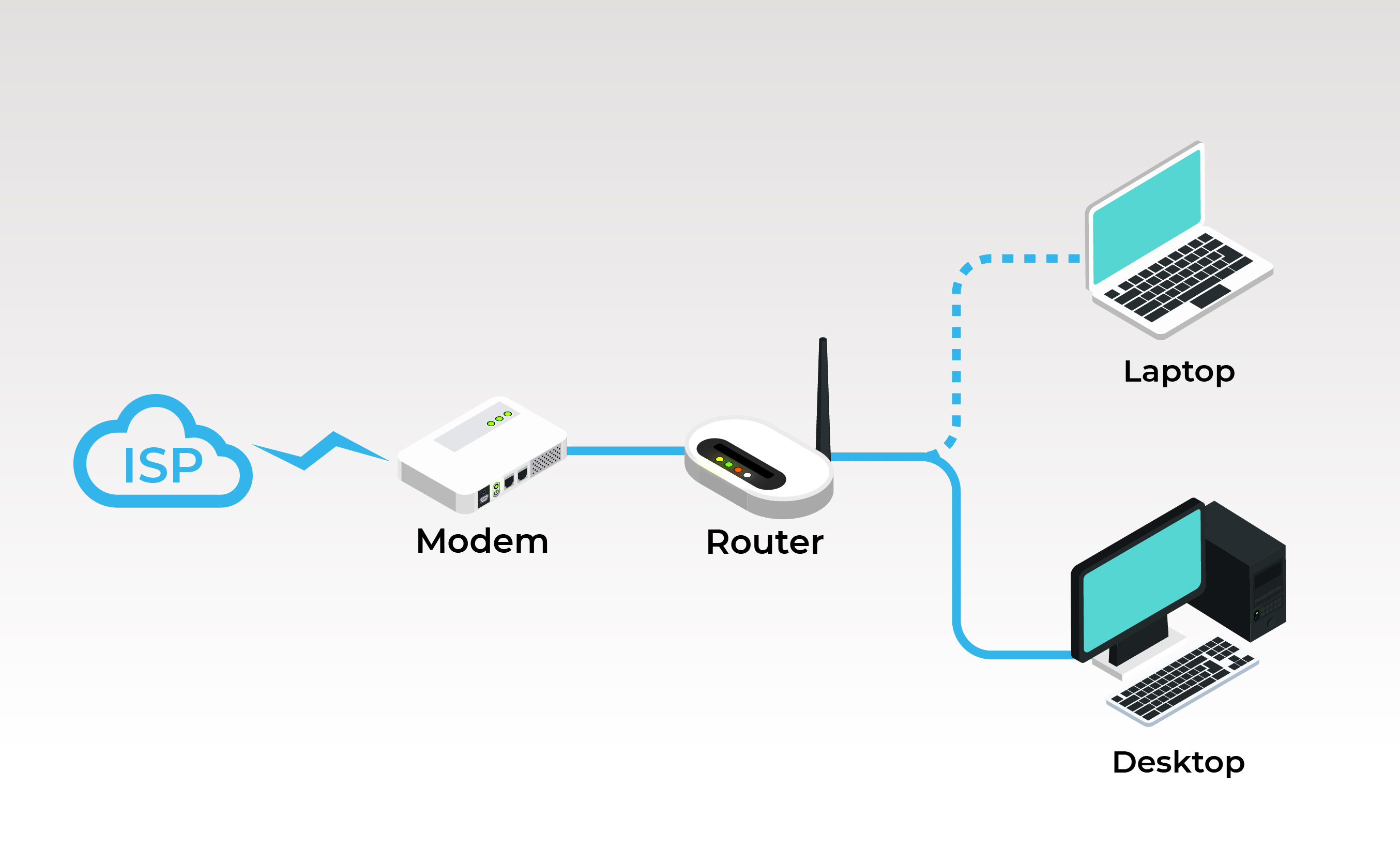
2. ISP —— Modem—— Router—— Desktop
Between the modem and the terminal device, the addition of a router allows multiple computers to access the Internet at the same time, and in the case of a wireless router, your mobile terminal can also be connected to the network.
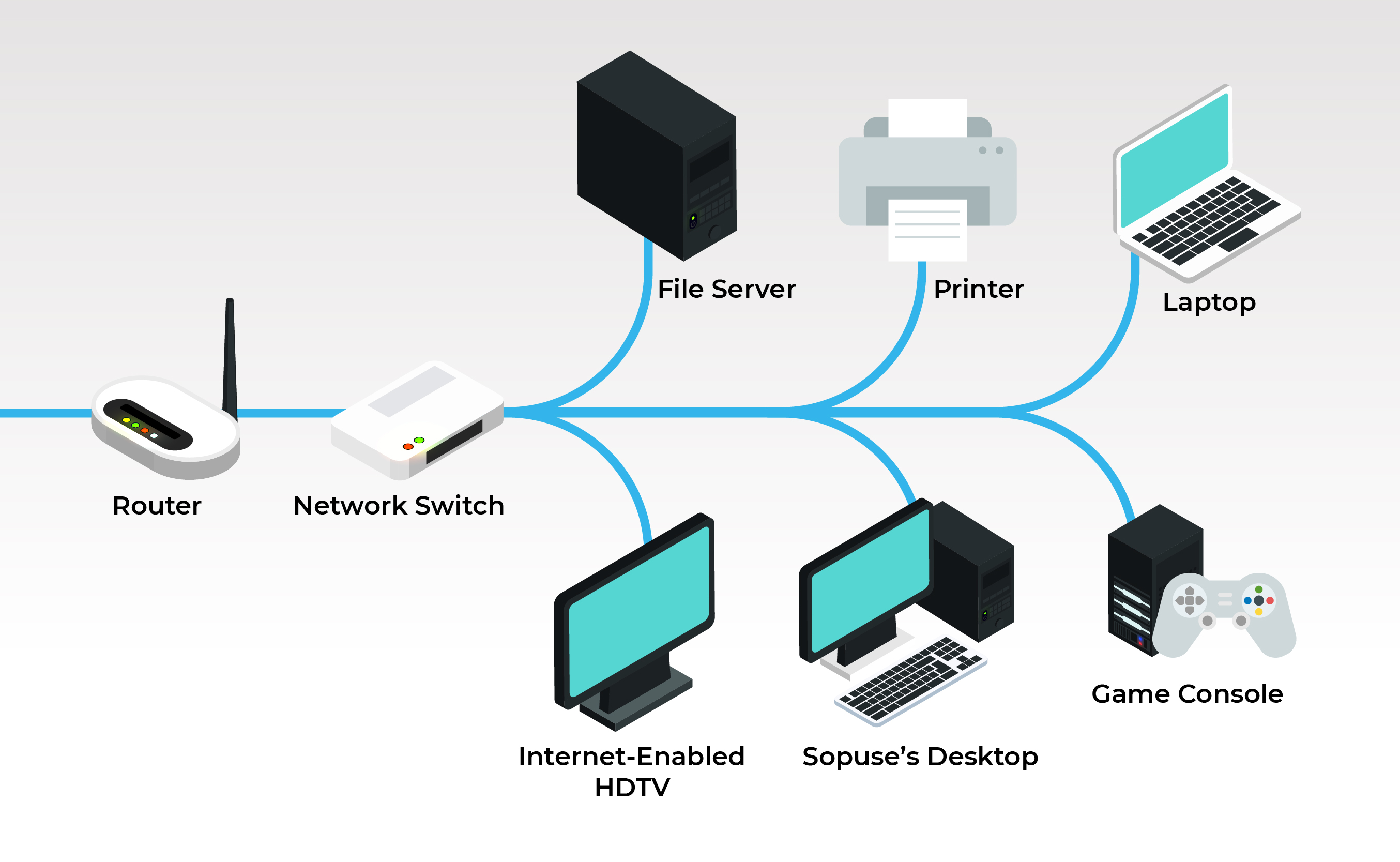
3. ISP —— Modem——Router——Switch——Desktop
A switch can form a small LAN of connected devices, which can then be connected to an external network through a router.
About hub
A network hub is a node that broadcasts data to every computer or Ethernet-based device connected to it. A hub is less sophisticated than a switch, the latter of which can isolate data transmissions to specific devices.Network hubs are best suited for small, simple local area network (LAN) environments.
Hubs cannot provide routing capabilities or other advanced network services. Because they operate by forwarding packets? across all ports indiscriminately, network hubs are sometimes referred to as "dumb switches." With limited capabilities and poor scalability, network hubs had primarily one competitive advantage over switches: lower prices.
As switch prices fell in the early to mid-2000s, hubs began getting phased out of use. Today, hubs are far less commonly deployed. But network hubs have some niche uses and continue to offer a simple means of networking.
About access point
Wireless AP (Access Point) that is, wireless access point, which is a wireless switches used for wireless networks, but also the core of the wireless network. Wireless AP is a mobile computer users into the wired network access point, mainly used for broadband homes, buildings and parks within the typical distance coverage of dozens of meters to hundreds of meters, the current main technology for the 802.11 series.
An AP connects directly to a wired local area network, typically Ethernet, and the AP then provides wireless connections using wireless LAN technology, typically Wi-Fi, for other devices to use that wired connection. APs support the connection of multiple wireless devices through their one wired connection.
Most of the wireless AP also has an access point client mode (AP client), and other AP can be connected wirelessly to extend the coverage of the network.
About gate way
Gateway, also known as inter-network connectors and protocol converters. Gateway in the transport layer in order to realize the network interconnection, is the most complex network interconnection equipment, only for the two high-level protocols are different network interconnection.
The structure of a gateway is also similar to that of a router, with the difference being the interconnection layer. Gateways can be used to interconnect both WANs and LANs. A gateway is a computer system or device that acts as a switching heavyweight.
A gateway is a translator between two systems that use different communication protocols, data formats or languages, or even have completely different architectures. Unlike a bridge that simply conveys information, a gateway repackages the information it receives to suit the needs of the destination system.
Also, gateways can provide filtering and security features. Most gateways run at the application layer, the top layer of the OSI 7-layer protocol.
FAQ
1. Can a modem also be a router?
Routers and modems have traditionally been two separate devices that worked together to form your home network. However, with modern technology, you do now no longer need a separate modem and separate router necessarily, as new combination of modem and router devices merge the two devices' features into one effective gadget.
2. Can a modem and router be next to each other?
A modem is usually placed near your main network jack. Most people keep their modem and router near each other for convenience, but it doesn't have to be that way. Even if you have a 2-in-1 modem and router or a gateway, you can get a better Wifi by putting the modem or router away.
3. Can modem go straight to switch?
Sure, you can connect a switch to the modem's Ethernet to provide Internet access to your devices, just like computers. The number of computers that can connect to the Internet depends on the number of interfaces that the switch has.
4. Do you need a router if you have a modem and switch?
Yes. A switch handles only the connections within the LAN, while a modem is only used to convert signals, and a router is the component connecting two different networks (the LAN or LSN and the Internet).
5. Can I use a modem with a switch instead of a router?
You need to connect the router to the modem because the router acts as an intermediary device that can indirectly connect many devices to the modem. When you add a device to a router, the router can assign a LAN IP address. A switch, on the other hand, only serves the function of assigning a network to a device.
Conclusion
We believe that you may have had a general understanding to Modem vs. Switch vs. Router. However, the best device must be the one that meet your demand, so please think twice before the purchase. If you like this blog, please share it with your friends, and make sure to make some comments below!