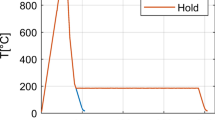
Isothermal and thermokinetic martensitic transformations in low-carbon martensitic steels have been studied. Amodel is proposed that relates the mechanical state of the austenite, as dependent on the parameters of thermal treatment and the law of the grain size distribution, to the volume fraction of transformed martensite. Physical constants of the transformation are determined.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. V. Kurdyumov and B. Ya. Lyubov, Kinetic Theory of Phase Transformations [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1966), 264 p.
Ya. S. Umanskii, B. N. Finkel’shtein, M. E. Blanter, et al., Physical Principles of Metallography [in Russian], GONTI, Moscow (1955), 724 p.
M. P. Kashchenko and V. G. Chashchina, Dynamic Theory of γ – α Martensitic Transformation in Iron Alloys and Solution of the Problem of Critical Grain Size [in Russian], Regular and Chaotic Dynamics Research Center – Izhevsk Institute of Computer Investigations, Moscow – Izhevsk (2010), 132 p.
V. I. Izotov, “Morphology and crystal geometry of lath (massive) martensite,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 34(1), 123 – 132 (1972).
V. M. Schastlivtsev, L. B. Blind, D. P. Rodionov, and I. L. Yakovleva, “Lath martensite structure in structural steels,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 66(4), 759 – 769 (1988).
Yu. G. Andreev, L. N. Devchenko, E. I. Zarkova, and M. A. Shtremel’, “Crystal geometry of martensitic shift in a large lath,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 56(4), 783 – 790 (1983).
M. A. Shtremel’, Yu. G. Andreev, and D. A. Kozlov, “Lath martensite structure and strength,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 4, 10 – 15 (1999).
V. M. Schastlivtsev, “Martensite structure peculiarities in structural steels,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 33(2), 326 – 334 (1972).
L. V. Karabasova, M. N. Spasskii, and M. A. Shtremel’, ”Hierarchy of low-carbon martensite structures,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 37(6), 1238 – 1248 (1974).
A. F. Edneral, V. I. Izotov, L. M. Kleiner, et al., ”Low-carbon martensitic steels,” in: Problems of Metal Science and Physical Metallography [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1972), pp. 123 – 134.
L. M. Kleiner, A. A. Shatsov, D. M. Larinin, and M. G. Zakirova, ”Low-carbon martensite structure and structural strength of martensitic steels,” Perspekt. Mater., No. 1, 59 – 67 (2011).
Yu. F. Titovets, N. Yu. Zolotarevskii, A. N. Samoilov, et al., “Modeling the influence of austenite grain size change on the kinetics of γ → α transformation,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2, 29 – 36 (2010).
M. Umemoto, E. Yoshitake, and I. Taniura, “The morphology of martensite in Fe – C, Fe – Ni – C, and Fe – Cr – C alloys,” J. Mater. Sci., 18(10), 2893 – 2904 (1983).
D. A. Mirzaev and K. Yu. Okishev, “Kinetic theory of lath martensite formation,” Vestn. Yuzh. Ural. Gos. Univ., No. 21, 9 – 14 (2007).
D. A. Mirzaev, K. Yu. Okishev, V. M. Schastlivtsev, and I. L. Yakovleva, “Kinetics of bainite and lath martensite formation: I. Effect of lath structure,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 90(5), 55 – 65 (2000).
D. A. Mirzaev, K. Yu. Okishev, V. M. Schastlivtsev, and I. L. Yakovleva, “Kinetics of bainite and lath martensite formation: II. Effect of incomplete transformation,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 90(5), 66 – 74 (2000).
V. A. Lobodyuk and E. I. Éstrin, Martensitic Transformations [in Russian], Fizmatlit, Moscow (2009), 352 p.
D. A. Mirzaev and K. Yu. Okishev, “Lath martensite formation in iron–nickel steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 9, 7 – 14 (2014).
Donghwi Kim, Seok-Jae Lee, and Bruno C. de Cooman, “Microstructure of low-C steel isothermally transformed in the M s to M f temperature range,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 43, 4967 – 4983 (2012).
T. Y. Hsu (Xu Zuyao), “Carbon diffusion and kinetics during the lath martensite formation,” J. Phys. IV France, 5, C8-351 – C8-354 (1995).
P. O. Bykova, L. M. Kleiner, A. A. Shatsov, and D. M. Larinin, “Modeling isothermal transformation of low-carbon austenite,” Meterialovedenie, No. 5, 10 – 14 (2013).
M. E. Blanter, Theory of Heat Treatment [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1984), 328 p.
S. A. Saltykov, Stereometric Metallography [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1976), 272 p.
S. L. Alhnazarova and V. V. Kafarov, Methods of Experiment Organization in Chemical Technology [in Russian], Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow (1985), 319 p.
I. V. Ryaposov, L. M. Kleiner, A. A. Shatsov, and E. A. Noskova, “Grain and lath martensite structure formation by thermal cycling in low-carbon martensitic steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 9, 33 – 39 (2008).
I. V. Ryaposov, L. M. Kleiner, and A. A. Shatsov, “Volume nanostructurization of low-carbon martensitic steels by heat treatment,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 9, 9 – 14 (2012).
J. Christian, The Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys, Part I: Equilibrium and General Kinetic Theory, Pergamon Press, Oxford (1978).
H. K. Bhadeshia, Bainite in Steels, Cambridge University Press, London (2001), 454 p.
L. M. Kleiner, D. M. Larinin, L. V. Spivak, and A. A. Shatsov, “Phase and structure transformations in low-carbon martensitic steels,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 108(2), 161 – 168 (2009).
D. L. Merson (ed.), Advanced Materials: Structure and Methods of Investigation (Learning Aid) [in Russian], TGU – MISiS, Togliatti – Moscow (2006), 536 p.
N. J. Petch, in: Proc. Int. Conf. on Atomic Mechanisms of Fracture (April 12 – 16, 1959, Swampscott, MA, United States).
V. N. Arzamasov, V. A. Brostrem, N. A. Bushe, et al. (eds.), Construction Materials (A Handbook) [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1990). 688 p.
W. Dahl and W. Anton (eds.), Static Strength and Fracture Mechanics of Steels [in German], Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf (1983).
A. M. Borzdyka and L. B. Gertsov, Stress Relaxation in Metals and Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1978), 272 p.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (Agreement No. 02.G25.31.0068 of 23.05.2013) in the framework of investigations according to Governmental Order No. 218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 8 – 14, August, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berezin, S.K., Shatsov, A.A., Bykova, P.O. et al. Martensitic Transformation in Low-Carbon Steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 59, 479–485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-017-0175-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-017-0175-0